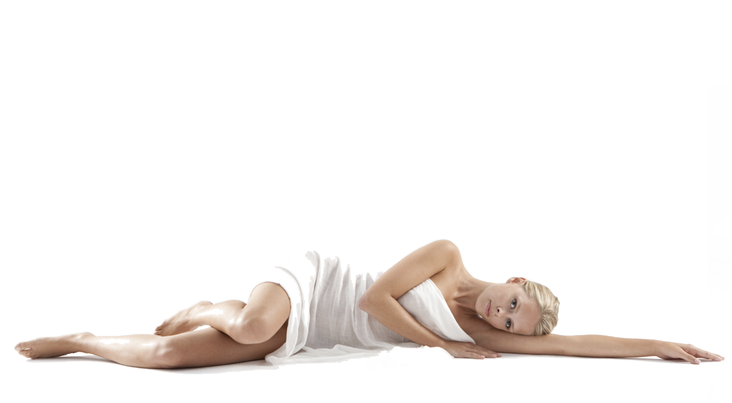
During adolescence, and especially around puberty, many women start to develop small pockets of fat above the pubic bone in the area known as the mons pubis.
This rounded deposit of fatty tissue naturally forms over the pubic bones and varies in size, depending on hormone levels and body fat. Generally, once pubic hair grows, this area becomes less visible, but for some women, the mons pubis can enlarge to a size that feels embarrassing and can even make it difficult to wear comfortable clothing.
While this fat deposit is natural, certain factors can lead to the enlargement of this area, including:
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Aging
- Genetics
Some men also find they develop fat in this area and choose to undergo treatment to create a slimmer and more attractive pubic area. The mons pubis area is often treated with liposuction along with abdominal treatment. For women who have given birth, vaginal muscles tend to stretch during childbirth, resulting in a larger opening and vaginal canal and weakened muscles.
The aging process can also lead to weakened and loose vaginal muscles. This can be uncomfortable and even embarrassing. Weak vaginal muscles can lead to sexual issues or dissatisfaction for both partners, and in the long term, even stress incontinence. Although specific exercises are designed to strengthen vaginal muscles, they often do not produce the desired results.
Childbirth can cause muscle damage, nerve impairment, and fibrosis in the vaginal area. Complaints from women who are potential candidates for vaginoplasty include:
- Desire to improve the appearance of the genital area
- Wanting to restore self-esteem and regain confidence
- Wishing to rejuvenate their intimate life
What is Vaginoplasty?
This is a cosmetic procedure that tightens the vaginal muscles, which may have become loose due to childbirth. It can also improve intimacy for women, which is why it is often referred to as a “designer vagina.”
Vaginoplasty can be performed with other procedures, such as labiaplasty (surgery on the inner or outer labia of the vagina).
Result and Aftercare
The duration of surgery varies depending on the number of targeted areas, approximately 1 to 2 hours. The patient will require local anesthesia during the surgery. Patients may need one to two weeks off. Some may experience deep pain in the first few days and should avoid tampons or intercourse for eight weeks. Depending on the degree of tightening, some patients may be advised to use dilators. Patients should gradually increase activity once they can sit without pain. With your doctor’s permission, you may return to work after three to five days, depending on the nature of your job, as you should avoid intense exercise.
 Română
Română  English
English  Français
Français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands 